Anti-stress effect (by human double-blind study)
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19(15): 8936.
To assess the current mood state of study, 66 healthy males and females at the age of 20 years or older were participated and divided in to three groups: placebo, low-dose SNK (50 mg: 100 billion bacteria cells), and high-dose SNK (150 mg: 300 billion bacteria cells). As a result of the analysis both SNK low dose and SNK high dose showed significantly lower TMD score compared to placebo.

(method)
Each group ingested for 4 weeks and analyzed by POMS2 psychological evaluation 2 was conducted after stress load (Uchida-Kraepelin test) before and after 4 week-intake. The amount of change the amount of change in the TMD score, which represents Total mood disturbance state was measured as the primary outcome.
*POMS2: Mood Profile Test to Assess the Mood State in a Time Frame by using seven scales: [Anger – Hostility] [Confusion – Bewilderment] [Depression – Dejection] – [Fatigue – Inertia] [Tension – Anxiety] (Vigor-Activity] [Friendliness] in addition to TMD
Increase the action of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)
Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry ,Published online 15 Sep 2019.
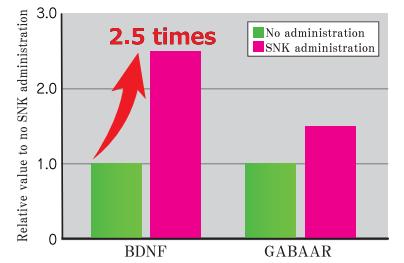
BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) is involved in cognition, learning and memory as well as differentiation and development of the nervous system. A reduction in BDNF in the brain hippocampus is associated with the occurrence of mood disorder and the BDNF level also decreases in a state of depression. Our verification test confirmed that the BDNF in the brain hippocampus of a stressed mouse increased with the administration of SNK, and the intake of SNK is expected to improve stress and depression.

Although BDNF decreases in a state of stress, the level of mRNA expression of the neurotrophic factor BDNF in the brain hippocampus of the stressed mice to which SNK was administered was 2.5 times higher than that of mice to which no SNK was administered.
It was also observed that the level of expression of the mRNA of the GABAA receptor also tended to increase.
Protective effect against influenza infection
Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2021, 40, 43–49.
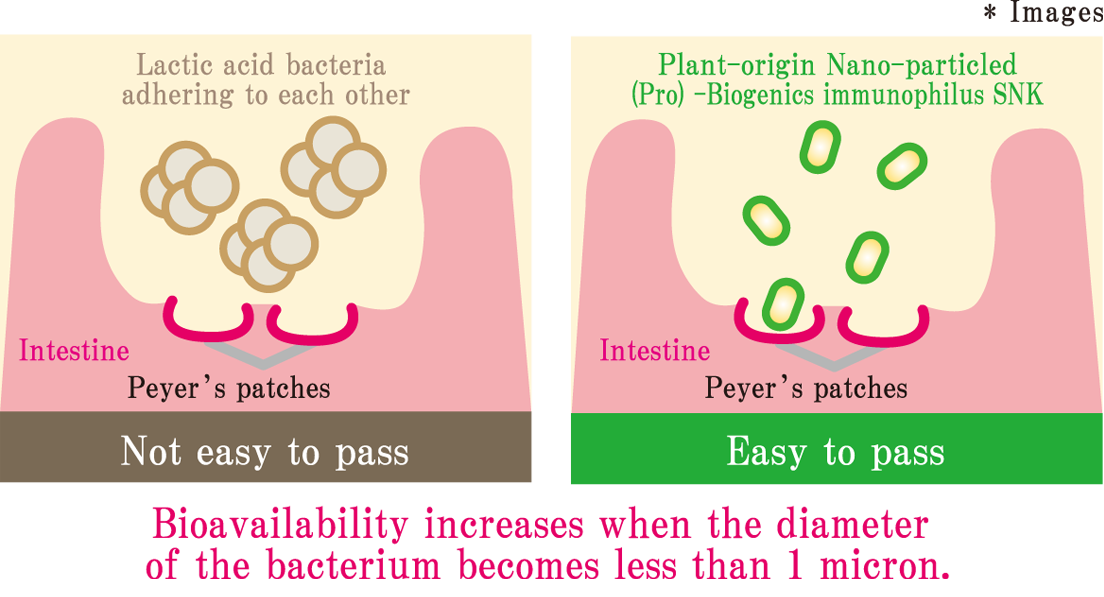
Protective effect of the oral intake of plant-derived nano-sized lactic acid bacteria SNK against influenza infection was confirmed.

Evaluation 3 days after infection
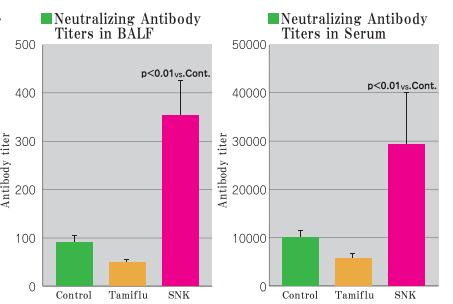
Regarding the quantity of the virus in the respiratory tract and lung 3 days after infection, it was confirmed that the influenza virus was remarkably inhibited in the SNK group compared to the Control group.

Evaluation 14 days after infection
Regarding the neutralizing antibody titer, which shows the strength of the immunity against the virus in the serum and respiratory tract 14 days after infection, the SNK group showed a higher value than the Control and Tamiflu groups.
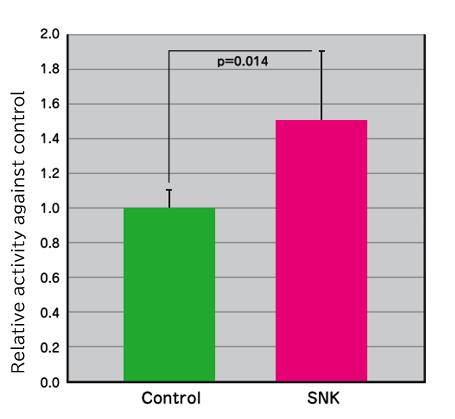
Effects on NK cell activity
It was confirmed that intake of plant-origin nano sized lactic acid bacterium SNK significantly increases the effects on NK cell activity.
(Test method)
6 week-old female BALB/C mice(n=6) were forcedly orally administered with SNK (1 mg/kg BW) and physiological saline (control) for 7 days, after the administration for 7days NK activity of spleen was measured.
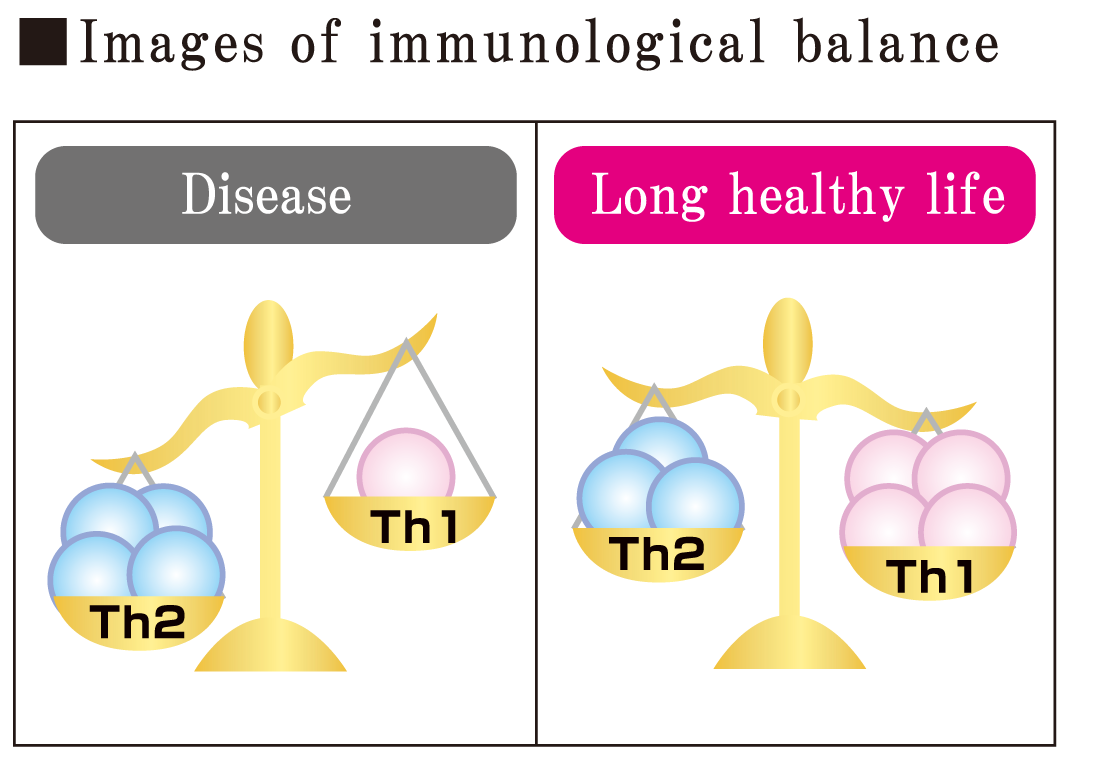
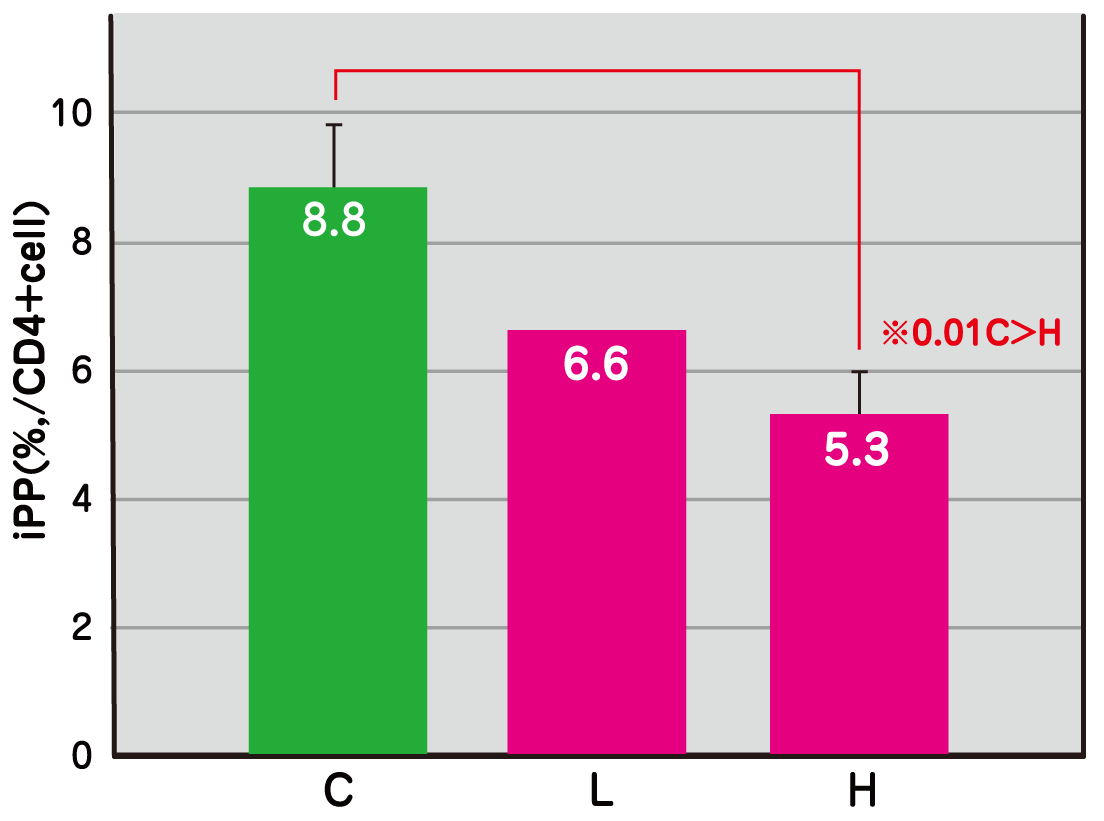
Inhibition of Th17 cell production (Peyer’s patch of mouse ileum)
With the continuous use of the plant-origin nano-sized lactic acid bacterium SNK, the behavior of the immune system cells developing intestinal problems such as colitis was studied.
As a result, a significant dose-dependent inhibition of SNK in the production of Th17 cells, which is relates autoimmune diseases, was observed.
(Test Method)
30 mice were divided into 3 groups of 10 mice (C: only physiological saline solution, L: physiological saline solution + SNK 2mg/kg, H: physiological saline solution + SNK 10mg/kg) and were administered for 15 days. After oral administration for 10 days, dextran sodium sulfate, which induces colitis, was injected to cause inflammation. After dissecting 16 days after administration, analyses for each group were conducted to determine the ratios of Th17 cells and the gene expressions of transcription factor that are related to Th17 cells.


 日本語
日本語 簡体中文
簡体中文